Introduction:
Cargo, the backbone of global trade, plays a crucial role in connecting businesses and consumers across the world. From transporting goods by land, sea, or air, to facilitating the smooth flow of commerce, cargo has a significant impact on various industries and economies. In this blog, we will delve into the world of cargo, exploring its importance, evolving trends, and the key players involved in its seamless operation.
The Significance of Cargo:
Cargo serves as the lifeblood of global trade, enabling the movement of goods and services between countries. It plays a vital role in supporting economic growth, facilitating international commerce, and meeting the demands of consumers worldwide. From raw materials to finished products, cargo encompasses a wide range of goods that are transported across different modes of transportation.
Modes of Cargo Transportation:
a) Air Cargo: Air freight offers speed and efficiency, making it ideal for transporting time-sensitive and perishable goods. Airlines, cargo carriers, and freight forwarders work together to ensure the timely delivery of goods through dedicated cargo planes and air cargo hubs.
b) Sea Cargo: Sea freight is widely used for transporting large quantities of goods, especially bulk cargo and containerized shipments. Ports, shipping lines, and logistics providers collaborate to manage complex logistics operations, including loading, unloading, and navigating international waters.
c) Land Cargo: Road and rail transport play a crucial role in moving cargo within and between countries. Trucks, trains, and intermodal transportation systems are used to transport goods efficiently across various terrains, connecting production centers, distribution hubs, and end consumers.
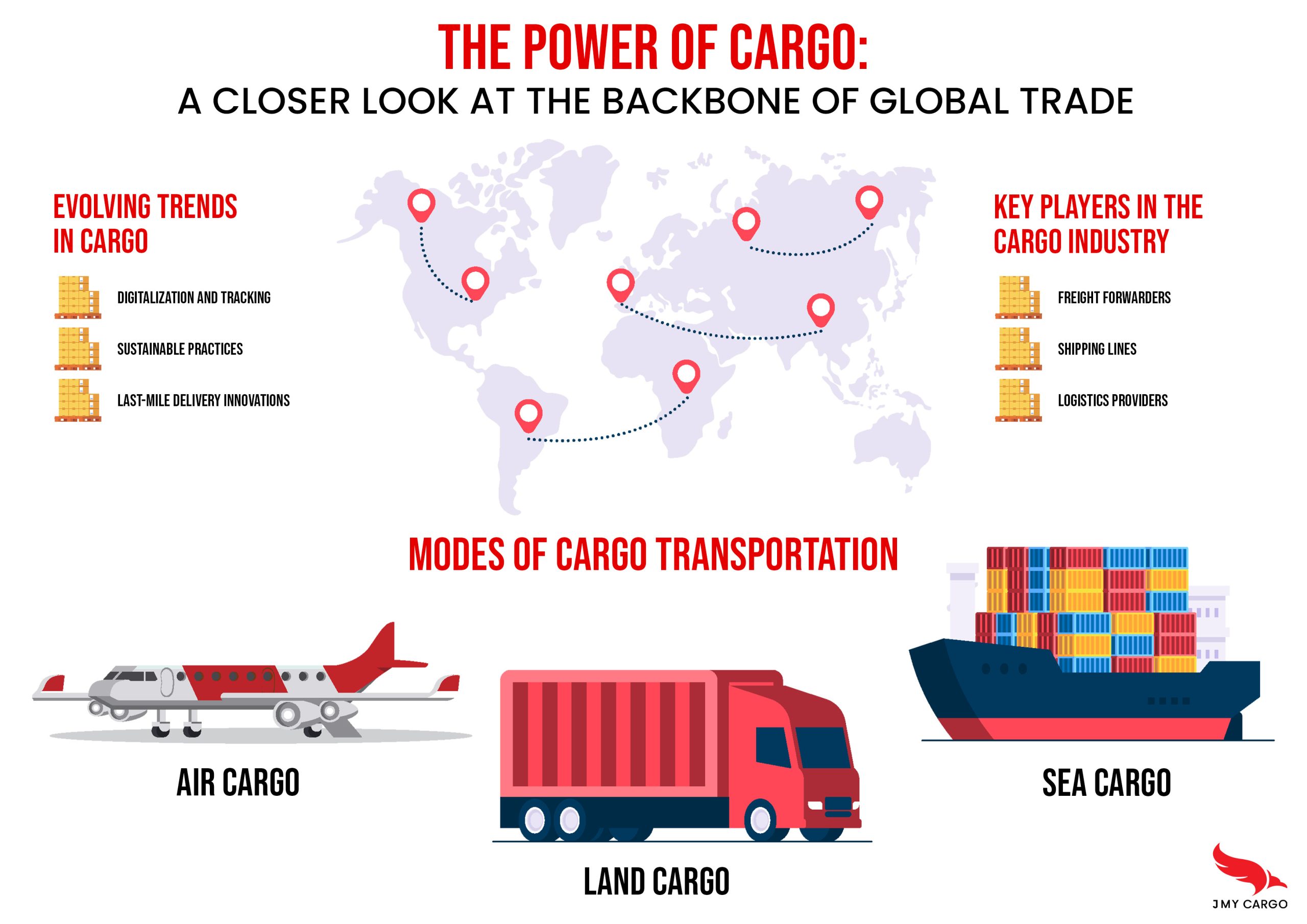
Evolving Trends in Cargo:
a) Digitalization and Tracking: Technology has revolutionized the cargo industry, with digital platforms and tracking systems providing real-time visibility and transparency. IoT devices, RFID tags, and blockchain solutions enable stakeholders to monitor cargo movements, optimize routes, and streamline documentation processes.
b) Sustainable Practices: As environmental concerns grow, the cargo industry is embracing sustainable practices. From the use of eco-friendly fuels and energy-efficient transportation to reducing carbon emissions, stakeholders are increasingly adopting greener alternatives to minimize their environmental impact.
c) Last-Mile Delivery Innovations: With the rise of e-commerce and consumer expectations for faster deliveries, last-mile logistics have become a focal point. Companies are experimenting with autonomous vehicles, drones, and innovative delivery models to enhance efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Key Players in the Cargo Industry:
a) Freight Forwarders: These intermediaries play a crucial role in coordinating cargo movements, managing logistics, and ensuring compliance with customs regulations. They act as a link between shippers, carriers, and other stakeholders involved in the transportation process.
b) Shipping Lines: As the backbone of maritime trade, shipping lines operate fleets of vessels, manage global shipping routes, and handle cargo consolidation and documentation.
c) Logistics Providers: These companies offer a range of services, including warehousing, inventory management, distribution, and supply chain solutions. They optimize cargo flows, handle order fulfillment, and provide end-to-end logistics support.
Conclusion:
Cargo forms the foundation of global trade, connecting businesses and consumers across borders. Whether transported by air, sea, or land, cargo plays a pivotal role in driving economic growth, enabling the exchange of goods, and meeting the demands of a globalized world. As the cargo industry continues to evolve, embracing digitalization, sustainability, and innovative practices, it holds the potential to reshape the future of commerce, offering faster, more efficient, and environmentally conscious transportation